date: 2022-10-10
Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition
This paper introduced method called a residual connection, which is also known as skip-connection, or shortcut.
Problem of deeper layers
Network depth became the crucial thing to consider when building visual recognition models.
However, two problems arises when we want to build better networks by stacking more layers.
First of all, vanishing gradient problem arises. This hampers convergence. This paper says that this problem can be largely solved by weight initialization by normalization and intermediate normalization layers (e.g. batch normalization). This two methods were two things that were not mentioned in VGG paper, but implemented in torchvision’s VGG model. I guess these two methods were used to address vanishing gradient problem.
Also, degradation problem arises. This problem is a situation confronted when the depth of networks becomes deeper, but accuracy gets saturated and then degrades rapidly. Adding more layers to a suitably deep model leads to higher training error.
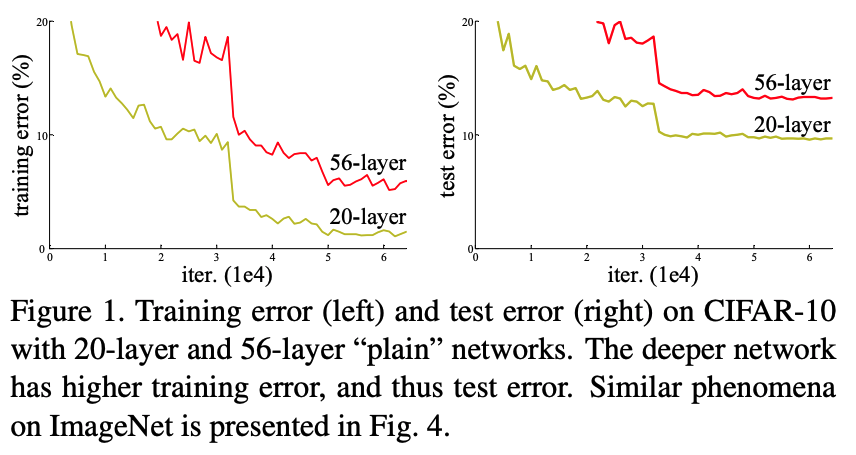
Deep Residual Learning Framework
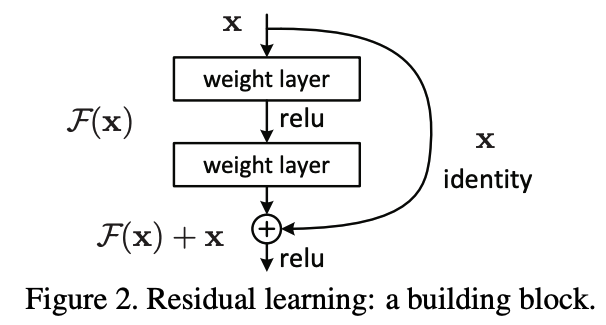
To talk about deep residual learning framework, let’s talk about residual learning first.
If we assume that $H(x)$ is the underlying mapping to be fit by a few stacked layers, when $x$ is the inputs to the first of these layers. The deep learning hypothesizes that multiple nonlinear layers can asymptotically approximate complicated functions, and thus they can also approximate residual function, which is $F(x)=H(x)-x$. Conclusively, we let multiple non-linear layers to approximate a residual function $F(x)$. So, the original function becomes $H(x)=F(x)+x$.
Identity Mapping by Shortcuts
In residual learning to every few stacked layers, one of the building blocks stated below is being used.
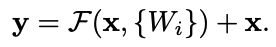
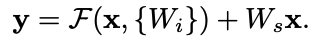
x and y represents the input and output vectors of the layers considered. And the function $F(x, {W_i})$ represents the residual mapping to be learned. and the operation $F+x$ is performed by a shortcut connection and element-wise addition. This shortcut connection introduce neither extra parameter nor computation complexity.
Since the shortcut connection needs a precondition that the two vectors to have a same dimension, a linear projection $W_s$ can be used to match dimensions.
The element-wise addition is performed on two feature maps, channel by channel.
Implementation
Image Preprocess:
- Resized with its shorter side randomly sampled in [256, 480] for scale augmentation.
- 224x224 crop is randomly sampled from an image or its horizontal flip
- per-pixel mean subtracted.
- standard color augmentation is used
BN
Experiments
ImageNet Classification
Used 1x1 conv to make network deeper.