date: 2022-11-15
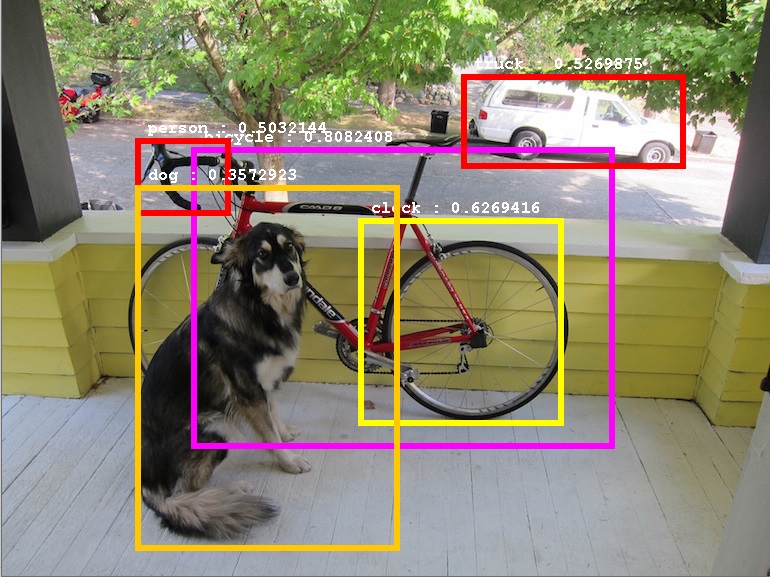
2 Stage Detectors
R-CNN, SPPNet, Fast R-CNN, and Faster R-CNN
R-CNN
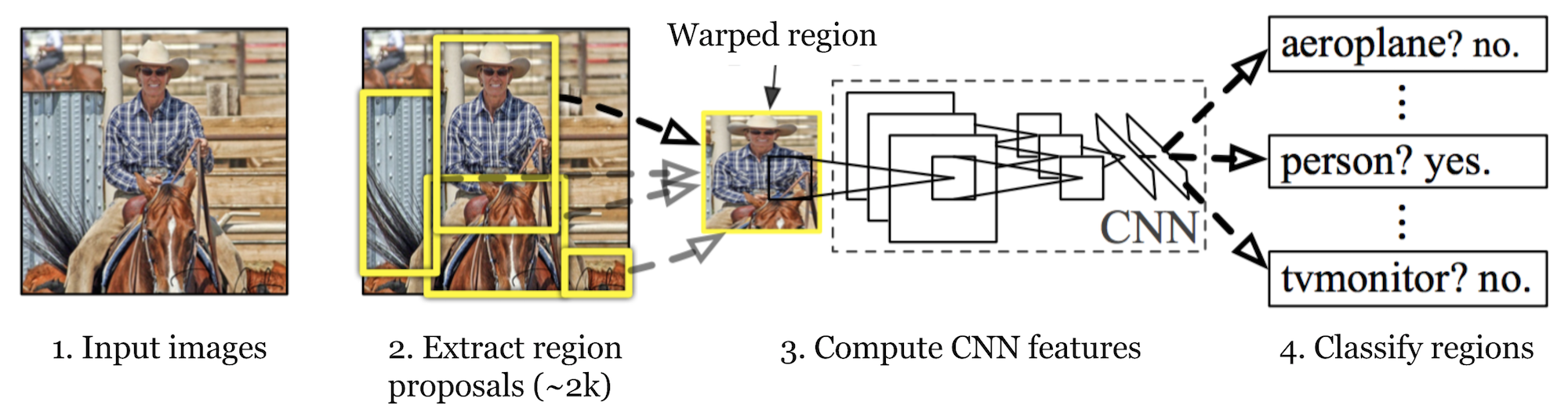
- Input image
- Extract Region Proposals
- Sliding window
Computationally very expensive.
need to search for object in thousands of windows even for a small size.
-
Selective search
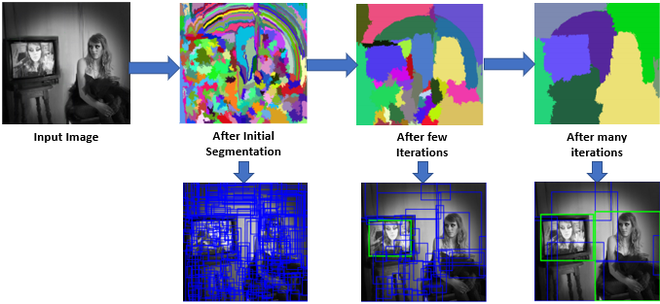
Generate many random bounding box. Merge bit by bit through multiple iterations.
Get 2000 regions from one input image.
Warp the regions into same size (224x224) to put into CNN model.
- Compute CNN features
- Classify Regions
SPP-Net
Image -> conv layers -> spatial pyramid pooling -> fc layers -> output
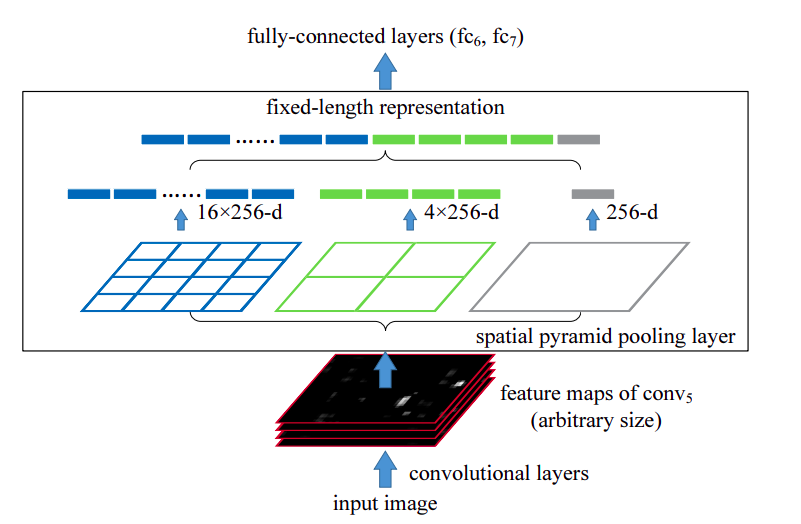
As for RNN, the input for fully connected layer had to be a fixed-length vector, so the warping process was necessary.
However, SPPNet made the model agnostic of input image size by replacing the pooling layer, which is in front of full-connected layer to spatial pyramid pooling layer (SPP).
In spatial pyramid pooling, we make the pooling window and stride be proportional to the imput image to get a fixed-sized output. This layer also applies a couple of different output sized pooling operations and combines the results before sending them to the next layer.
In the paper, the authors have used three pooling operations where one of them outputs only a single number for each map, other one gives a 2x2 grid output for each map, and the last one gives a 4x4 output.
Fast R-CNN
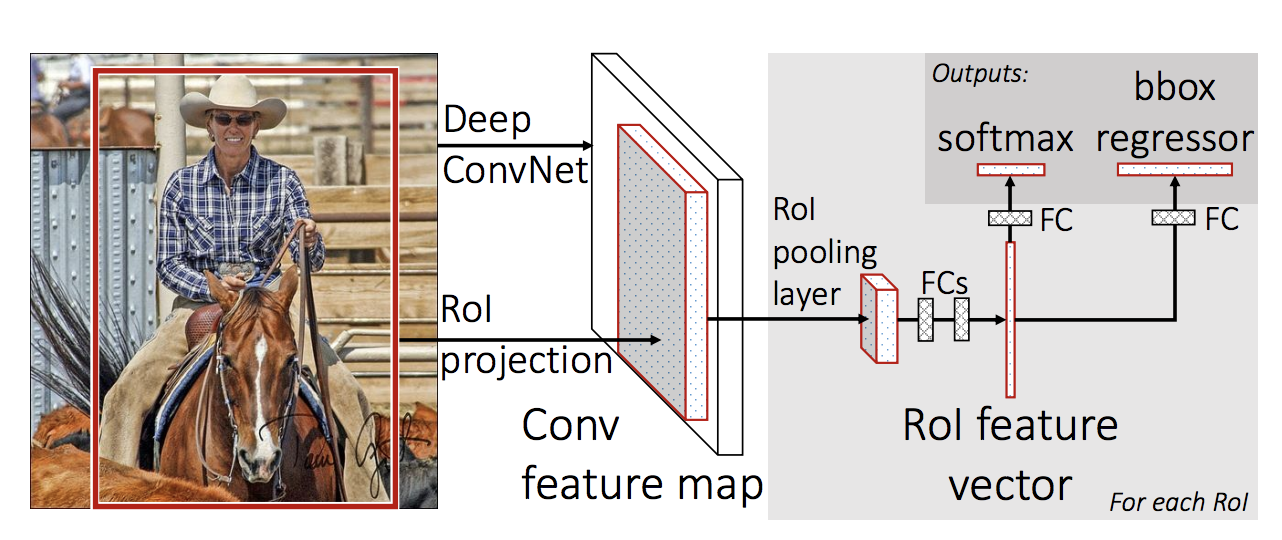
Pipeline:
- forward whole image through ConvNet to extract features.
-
compute RoI from the feature map through RoI Projection. Region of Interest(RoIs) are from a proposal method like selective search.
-
extract fixed sized feature through RoI Pooling.
This process is to get a fixed-size vector. We use SPP with pyramid level 1 and 7x7 target grid size.
-
After fully connected layer, the output is put through softmax classifier and bounding box regressor
The number of class is C+1 (number of class C + background)
Training:
In this paper, the authors use multi task loss, which is combination of classification loss and bounding box regression. Loss functions for classification and BB regressor are different, loss function for classification is cross entropy and loss function for BB regressor is smooth L1 loss.
Regarding dataset, positive samples are defined by IoU bigger than 0.5 and negative samples are defined by IoU bigger than 0.1 and smaller than 0.5. In one batch, positive samples are 25% of the whole and negative samples are 75% of the whole. One batch includes only RoIs of one image. Computations and memory can be shared inside one batch.
Shortcomings:
This is not an end-to-end algorithm.
Faster RCNN
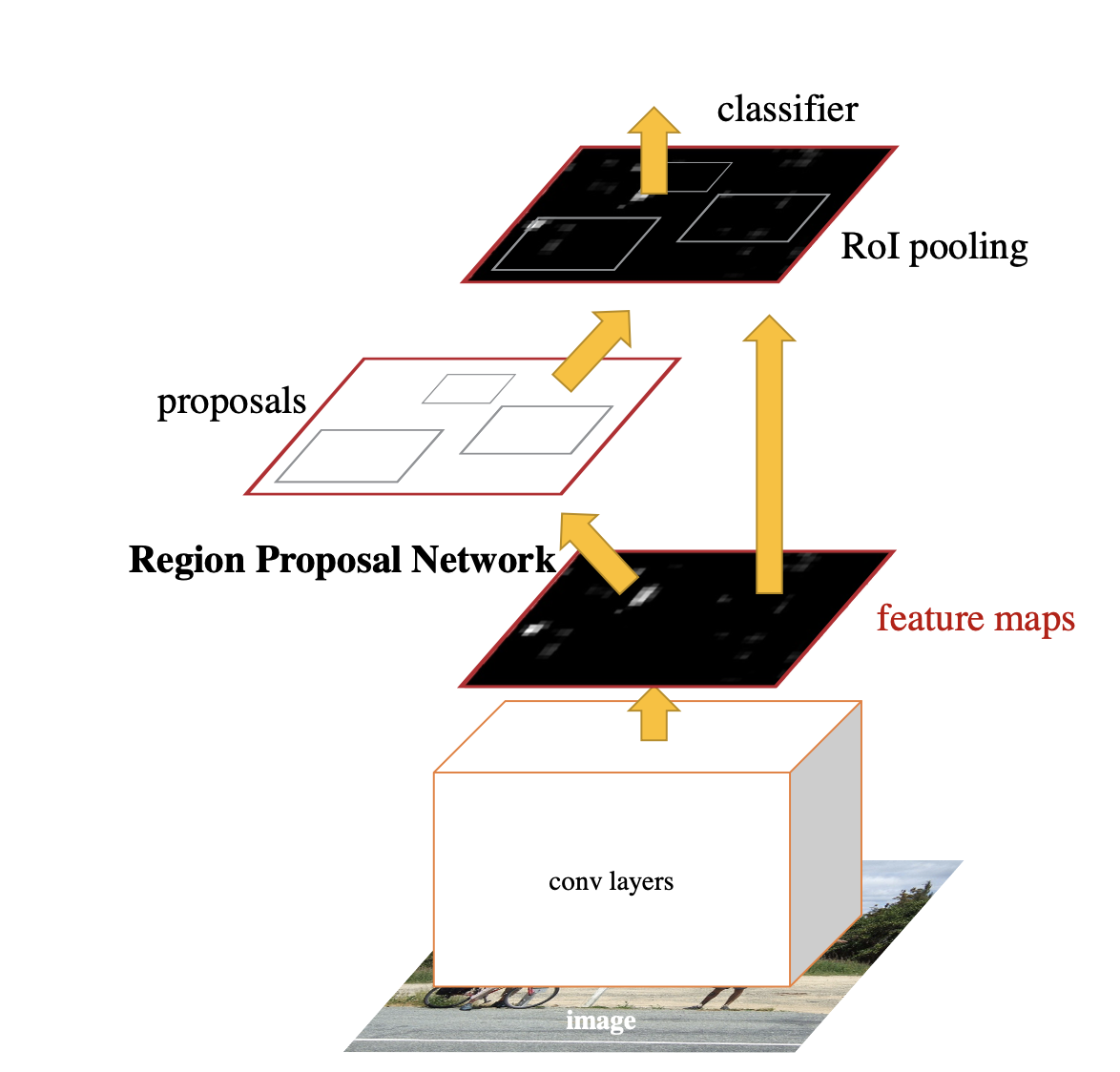
RoIs are proposed by selective search in Fast R-CNN. But, in Faster R-CNN, Region Proposal Network(RPN) is used to propose RoIs.
Through conv layers, we get feature maps. By dividing feature maps, we get cells from feature maps. For each cell, we can define k number of anchor boxes, which have different size and different views. In RPN, we decide whether or not each anchor box includes an object. If the anchor box includes an object, detailed adjustment of the bounding box is done.
References
Understanding SPPNet for Object Classification and Detection